Machine Learning
➣ Introduction
▸ Machine learning (ML) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
▸ Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output.
▸ Machine Learning is used anywhere from automating mundane tasks to offering intelligent insights, industries in every sector try to benefit from it.
▸You may already be using a device that utilizes it.
For example, a wearable fitness tracker like Fitbit, or an intelligent home assistant like Google Home.
➣ Examples of Machine Learning (ML)
⊛ Prediction -
Machine learning can also be used in the prediction systems.
Considering the loan example, to compute the probability of a fault, the system will need to classify the available data in groups.
⊛ Image recognition -
Machine learning can be used for face detection in an image as well.
There is a separate category for each person in a database of several people.
⊛ Speech Recognition -
It is the translation of spoken words into the text.
It is used in voice searches and more.
Voice interfaces include voice dialing, call routing, and appliance control.
It can also be used a simple data entry and the preparation of structured documents.
⊛ Medical diagnoses -
ML is trained to recognize cancerous tissues.
Financial industry and trading -
Companies use ML in fraud investigations and credit checks.
➣ A Quick History of Machine Learning
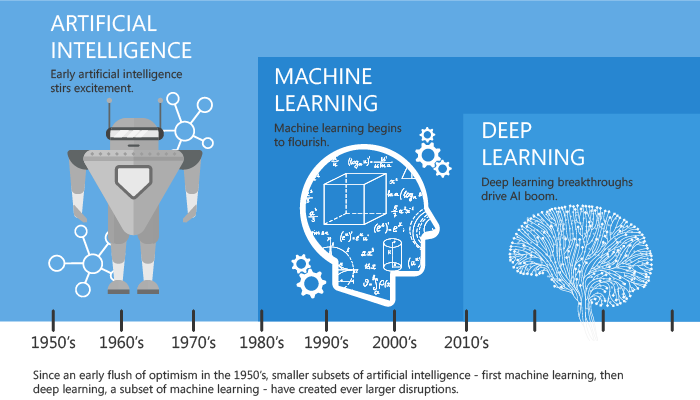
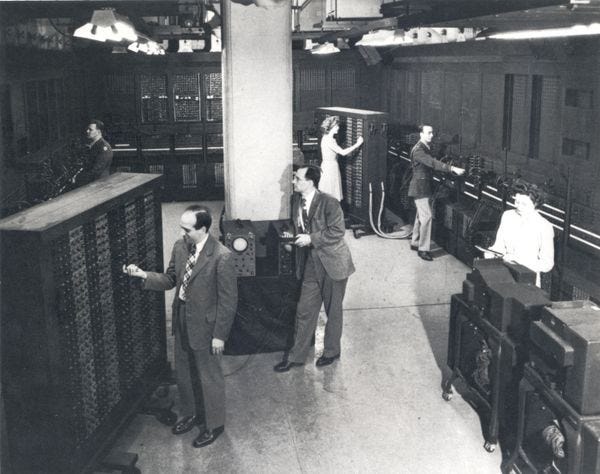
⇛ It was in the 1940s when the first manually operated computer system, ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), was invented.
⇛ At that time the word “computer” was being used as a name for a human with intensive numerical computation capabilities, so, ENIAC was called a numerical computing machine!
⇛ Well, you may say it has nothing to do with learning?! WRONG, from the beginning the idea was to build a machine able to emulate human thinking and learning.

⇛ In the 1950s, we see the first computer game program claiming to be able to beat the checkers world champion.This program helped checkers players a lot in improving their skills!
⇛ Around the same time, Frank Rosenblatt invented the Perceptron which was a very, very simple classifier but when it was combined in large numbers, in a network, it became a powerful monster.
⇛ Well, the monster is relative to the time and in that time, it was a real breakthrough.
Then we see several years of stagnation of the neural network field due to its difficulties in solving certain problems.
⇛ Thanks to statistics, machine learning became very famous in the 1990s.
⇛ The intersection of computer science and statistics gave birth to probabilistic approaches in AI.
⇛ This shifted the field further toward data-driven approaches.
⇛ Having large-scale data available, scientists started to build intelligent systems that were able to analyze and learn from large amounts of data.
⇛ As a highlight, IBM’s Deep Blue system beat the world champion of chess, the grand-master Garry Kasparov.
⇛ Yeah, I know Kasparov accused IBM of cheating, but this is a piece of history now and Deep Blue is resting peacefully in a museum.
➣ What is Machine Learning?
⇢ According to Arthur Samuel, Machine Learning algorithms enable the computers to learn from data, and even improve themselves, without being explicitly programmed.
⇢ Machine learning (ML) is a category of an algorithm that allows software applications to become more accurate in predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed.
⇢ The basic premise of machine learning is to build algorithms that can receive input data and use statistical analysis to predict an output while updating outputs as new data becomes available.
➣ Types of Machine Learning?
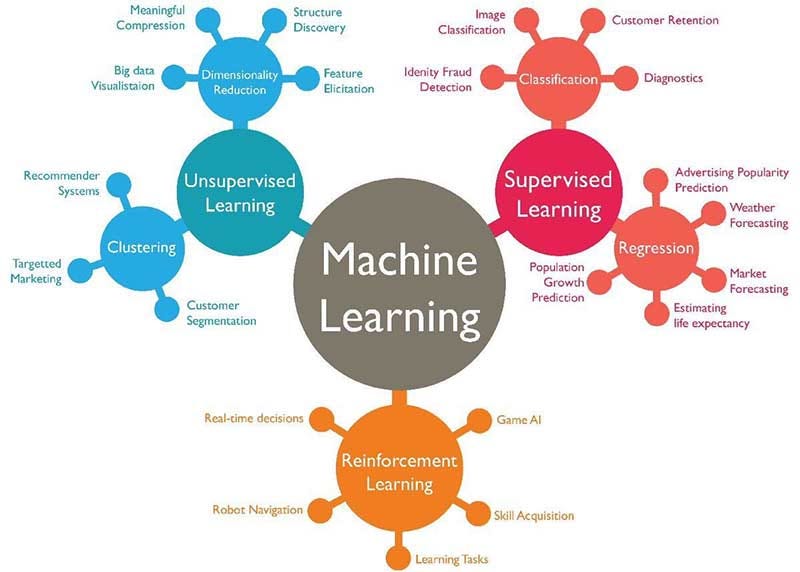
Machine learning can be classified into 3 types of algorithms.
1. Supervised Learning
2. Unsupervised Learning
3. Reinforcement Learning
➣ Overview of Supervised Learning Algorithm
⇝ In Supervised learning, an AI system is presented with data which is labeled, which means that each data tagged with the correct label.
⇝ The goal is to approximate the mapping function so well that when you have new input data (x) that you can predict the output variables (Y) for that data.
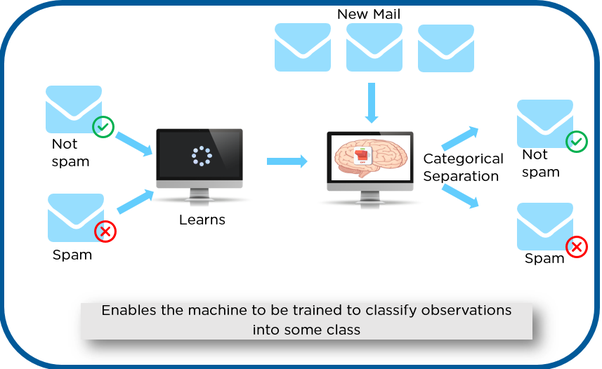
⇝ As shown in the above example, we have initially taken some data and marked them as ‘Spam’ or ‘Not Spam’.
⇝This labeled data is used by the training supervised model, this data is used to train the model.
⇝ Once it is trained we can test our model by testing it with some test new mails and checking of the model is able to predict the right output.
➣ Types of Supervised learning
◘ Classification:
A classification problem is when the output variable is a category, such as “red” or “blue” or “disease” and “no disease”.
◘ Regression:
A regression problem is when the output variable is a real value, such as “dollars” or “weight”.
➣ Overview of Unsupervised Learning Algorithm
⇨In unsupervised learning, an AI system is presented with unlabeled, uncategorized data and the system’s algorithms act on the data without prior training.
⇨The output is dependent upon the coded algorithms. Subjecting a system to unsupervised learning is one way of testing AI.
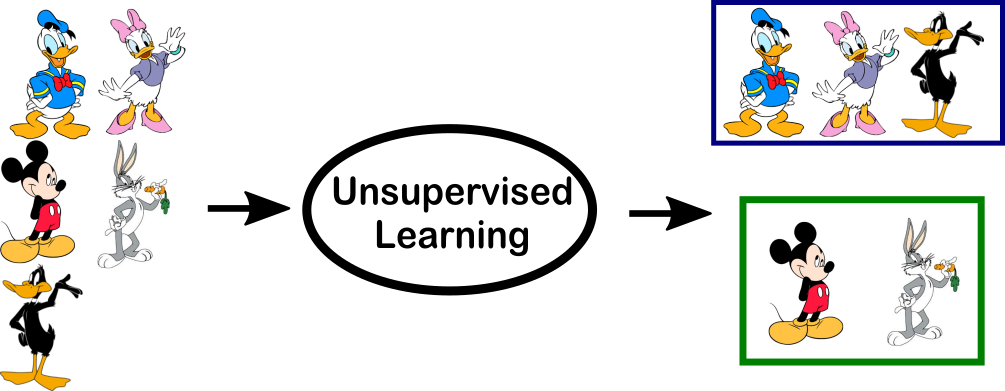
⇨In the above example, we have given some characters to our model which are ‘Ducks’ and ‘Not Ducks’.
⇨In our training data, we don’t provide any label to the corresponding data.
⇨The unsupervised model is able to separate both the characters by looking at the type of data and models the underlying structure or distribution in the data in order to learn more about it.
➣ Types of Unsupervised learning
▹ Clustering:
A clustering problem is where you want to discover the inherent groupings in the data, such as grouping customers by purchasing behavior.
▹ Association:
An association rule learning problem is where you want to discover rules that describe large portions of your data, such as people that buy X also tend to buy Y.
➣ Overview of Reinforcement Learning
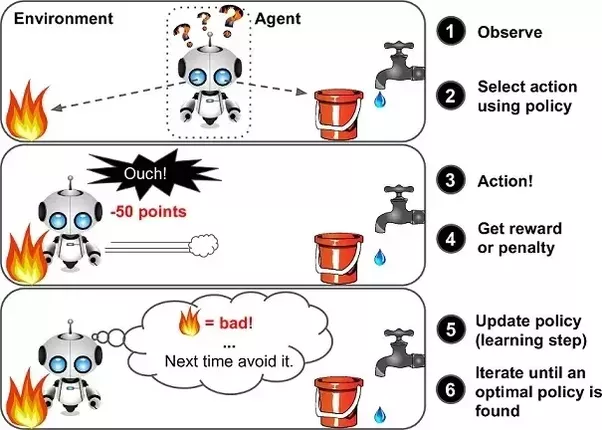
➔ A reinforcement learning algorithm, or agent, learns by interacting with its environment.
➔ The agent receives rewards by performing correctly and penalties for performing incorrectly.
➔ The agent learns without intervention from a human by maximizing its reward and minimizing its penalty.
It is a type of dynamic programming that trains algorithms using a system of reward and punishment.
➔ In the above example, we can see that the agent is given 2 options i.e. a path with water or a path with fire.
➔ A reinforcement algorithm works on reward a system i.e. if the agent uses the fire path then the rewards are subtracted and agent tries to learn that it should avoid the fire path.
➔ If it had chosen the water path or the safe path then some points would have been added to the reward points, the agent then would try to learn what path is safe and what path isn’t.
➔ It is basically leveraging the rewards obtained, the agent improves its environment knowledge to select the next action.







